Within the realm of ADHD, a tapestry of unanswered questions weaves its way through the fabric of scientific exploration. As researchers and clinicians delve into the complexities of this neurodevelopmental disorder, they unearth new insights while uncovering a plethora of mysteries that still elude our understanding. These unanswered questions invite us to embark on a voyage of discovery, seeking to unravel the enigmatic nature of ADHD and shed light on its intricacies.
One fundamental question that lingers pertains to the precise causes of ADHD. While genetic factors are known to play a significant role, there remains much to unravel regarding the interplay between genes, environmental influences, and brain development. What intricate mechanisms give rise to the unique neurobiological signature of ADHD? Are there specific environmental factors that contribute to its manifestation? By unravelling the complex tapestry of causality, we may gain a deeper understanding of the disorder’s origins and pave the way for more targeted interventions.
Another enigma lies in the heterogeneity of ADHD symptoms. Individuals diagnosed with ADHD can present with a wide range of manifestations, both in terms of symptom severity and specific symptom profiles. Why do some individuals primarily struggle with inattention, while others exhibit hyperactivity and impulsivity as dominant features? Are there distinct subtypes of ADHD that require tailored approaches to assessment and treatment? Unravelling the intricacies of this heterogeneity may lead to more personalised interventions and a deeper appreciation of the diverse experiences of those living with ADHD.
The long-term outcomes of ADHD also remain an open question. While the disorder is commonly associated with challenges in academic performance, social interactions, and occupational success, there is a need to understand the trajectories of individuals with ADHD throughout their lifespan. Do these difficulties persist into adulthood, or do individuals with ADHD develop unique strengths and coping mechanisms that enable them to thrive? By exploring the longitudinal course of ADHD, we may uncover insights into resilience, adaptive strategies, and the factors that contribute to positive outcomes.
Furthermore, the optimal approach to treatment for individuals with ADHD continues to evolve. While stimulant medication and behavioural interventions are commonly utilised, questions persist regarding their long-term efficacy, potential side effects, and the integration of alternative approaches. Are there non-pharmacological interventions that hold promise for certain individuals or specific symptom domains? How can we address the needs of individuals who do not respond favourably to standard treatments? By expanding our treatment repertoire, we may be able to provide more comprehensive and tailored support for individuals with ADHD.
As the horizon of knowledge expands, so too does the landscape of unanswered questions in the realm of ADHD. Each inquiry represents an opportunity for scientific exploration, fostering collaboration, and ultimately enhancing our understanding of this complex disorder. By peering into these mysteries with curiosity and dedication, we strive to bring clarity to the shadows, providing solace and empowerment to individuals living with ADHD and their families. Through collective efforts, we embark on a quest to unravel the unanswered questions and pave the way for a brighter future for those touched by ADHD.
1. Are ADHD People Friendly?
ADHD does not determine whether someone is friendly or not. Friendliness is a personality trait that can be found in individuals with or without ADHD. ADHD affects various aspects of a person’s life, including attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, but it does not define their social behaviour or ability to interact with others.
People with ADHD can exhibit a wide range of social characteristics, just like anyone else. Some individuals with ADHD may naturally possess a friendly and outgoing demeanour, enjoying social interactions and easily connecting with others. They may thrive in social settings, engaging in conversations, and forming meaningful relationships.
On the other hand, some individuals with ADHD may face challenges in social situations due to difficulties with impulsivity, inattention, or self-regulation. These challenges can sometimes impact their social interactions, leading to misunderstandings, interrupting others, or difficulty focusing on conversations. However, it’s important to note that these challenges are specific to ADHD symptoms and not indicative of a person’s inherent friendliness.
It’s crucial to remember that individuals with ADHD, just like anyone else, have their own unique personalities, strengths, and preferences when it comes to socialising. While ADHD can influence certain aspects of their behaviour, it does not determine their overall friendliness or likability. Understanding and accepting individuals with ADHD based on their individual traits and characteristics, rather than making assumptions based on their diagnosis, is essential for fostering positive relationships and connections.

2. What Are People With ADHD Good At?
While ADHD can present challenges in various aspects of life, individuals with ADHD also possess unique strengths and abilities. Here are some areas where people with ADHD often excel:
Creativity
Many individuals with ADHD have a remarkable ability to think outside the box and generate innovative ideas. Their minds often race with a constant flow of thoughts, which can lead to unique connections and unconventional approaches to problem-solving. This creativity can be channelled into artistic pursuits, entrepreneurship, or finding novel solutions in various domains.
Hyperfocus
While difficulty with sustained attention is a common trait of ADHD, individuals with ADHD can also experience periods of intense focus and concentration. This hyper-focus allows them to immerse themselves deeply in tasks or activities that captivate their interest. When they find something they are passionate about, they can exhibit exceptional productivity and exhibit an impressive level of skill and knowledge.
High Energy and Enthusiasm
The abundance of energy that often accompanies ADHD can be channelled into positive pursuits. Individuals with ADHD may possess contagious enthusiasm, bringing energy and excitement to projects and interactions. They can infuse a sense of vitality into group settings and inspire others with their zest for life.
Thinking on Their Feet
The impulsive nature of ADHD can lead to quick decision-making and the ability to adapt swiftly to changing situations. People with ADHD often possess strong intuition and can make connections and decisions rapidly, sometimes without the burden of overthinking. In dynamic environments or situations that require on-the-spot problem-solving, they can shine.
Multitasking and Handling Stimulating Environments
While multitasking can be challenging for many, individuals with ADHD often thrive in stimulating and dynamic environments. They can juggle multiple tasks or stimuli, processing information rapidly and engaging in parallel activities. This ability can be advantageous in certain professions, such as event management, emergency response, or creative industries.
Moreover, these strengths can vary from person to person, and not everyone with ADHD will excel in all these areas. Each individual with ADHD is unique and may have a combination of different strengths and talents. Recognising and harnessing these strengths can contribute to personal growth, success, and a sense of fulfilment for individuals with ADHD.

3. How Do I Check If I Have ADHD?
While I can provide some guidance, it’s important to note that I am an AI language model and cannot provide a diagnosis. If you suspect you may have ADHD, it is recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, who can conduct a comprehensive evaluation and provide an accurate diagnosis. However, here are some general steps you can take:
Educate yourself
Learn more about ADHD and its symptoms to gain a better understanding of the disorder. Reliable sources, such as reputable websites or books written by experts, can provide valuable information.
Self-reflection
Reflect on your own experiences and behaviours. Take note of any challenges you may have faced throughout your life, such as difficulties with attention, impulsivity, organisation, time management, or maintaining relationships. Consider how these challenges may be impacting your daily life and functioning.
Talk to others
Consult with trusted friends, family members, or close acquaintances who may have observed your behaviour over an extended period. They may be able to provide valuable insights and observations that can contribute to your understanding of your own experiences.
Seek professional evaluation
Schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional who specialises in ADHD evaluations, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. They will conduct a thorough assessment, which typically involves gathering information about your personal and medical history, symptoms, and any relevant observations. This may include interviews, questionnaires, and other assessment tools.
Collaborate with professionals
Work closely with the healthcare professional conducting the evaluation. Be open and honest about your experiences and symptoms. They will analyse the information gathered, compare it with the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition), and provide you with a diagnosis if applicable.
Remember, only a qualified healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis of ADHD. Seeking professional evaluation is crucial for obtaining appropriate support, treatment, and guidance tailored to your specific needs.

4. Who Is The Most Famous Person With ADHD
There are several well-known individuals who have publicly shared their experiences of living with ADHD. While it is difficult to pinpoint a single “most famous” person with ADHD, here are a few notable figures:
Simone Biles
The celebrated American gymnast and Olympic gold medallist, Simone Biles, has openly discussed her diagnosis of ADHD. Despite the challenges it presents, Biles has shown incredible resilience and achieved extraordinary success in her gymnastics career.
Michael Phelps
The most decorated Olympian of all time, Michael Phelps, has also spoken about his ADHD diagnosis. He has shared how swimming provided an outlet for his energy and helped him focus his attention.
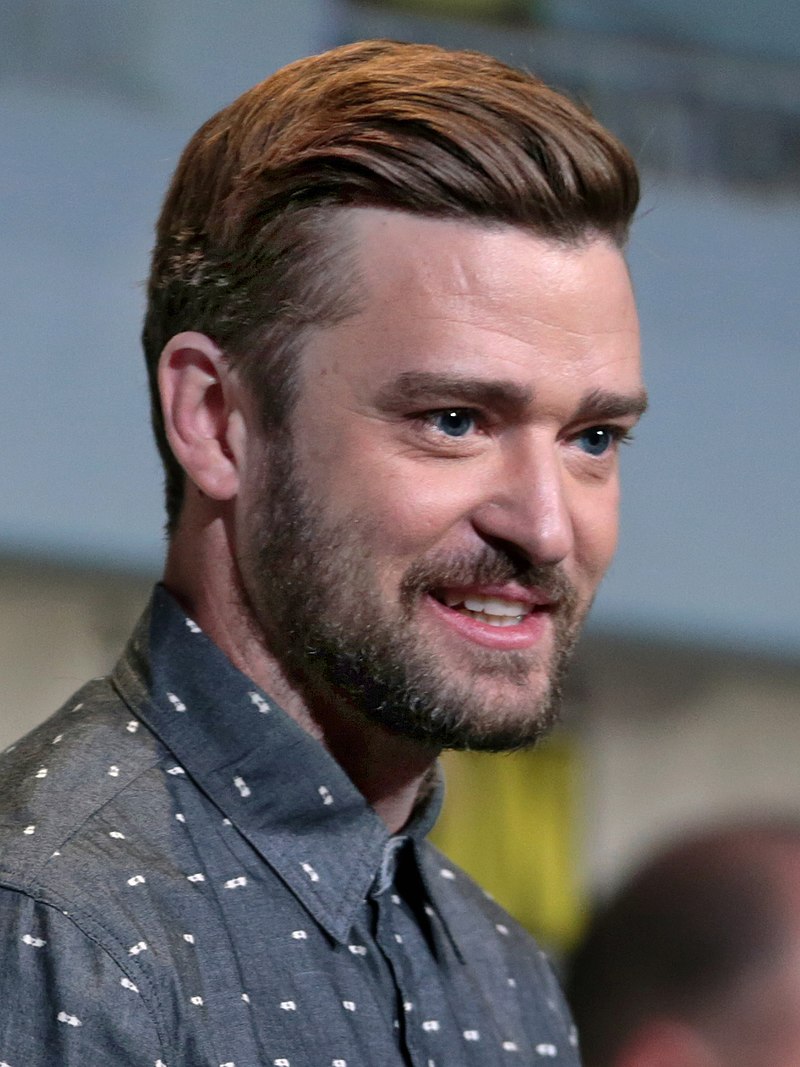
Justin Timberlake
The accomplished singer, songwriter, and actor Justin Timberlake has spoken about his experiences with ADHD. He has mentioned how ADHD influenced his ability to concentrate and engage in school while recognising the positive aspects of his energetic and creative nature.
Richard Branson
The renowned entrepreneur and founder of the Virgin Group, Richard Branson, has revealed his ADHD diagnosis. He has attributed his entrepreneurial success to his ability to think creatively, take risks, and find alternative solutions, which are traits commonly associated with ADHD.
Solange Knowles
Solange Knowles, an American singer, songwriter, and actress, has discussed her experience with ADHD. She has emphasised the importance of self-care and finding strategies to manage her symptoms while pursuing her creative passions.

5. How Do People With ADHD Sleep?
Sleep can be a challenge for some individuals with ADHD due to the various symptoms associated with the disorder. Here are some common sleep-related experiences and challenges that people with ADHD may encounter:
Difficulty Falling Asleep
Racing thoughts and a constant flow of ideas can make it challenging for individuals with ADHD to calm their minds and relax before sleep. It may take them longer to fall asleep compared to others.
Restlessness and Hyperactivity
The excess energy and restlessness often associated with ADHD can persist into the evening
making it harder for individuals to settle down and enter a state of relaxation conducive to sleep.
Delayed Sleep-Wake Schedule
People with ADHD may naturally have a delayed sleep-wake schedule, finding it difficult to fall asleep early and waking up later than desired. This can lead to difficulties in adhering to a regular sleep routine, especially if external obligations require an earlier waking time.
Sleep-Onset Insomnia
Some individuals with ADHD experience sleep-onset insomnia, where they struggle to initiate sleep even when they feel tired. This may be due to racing thoughts, worries, or difficulties in quieting the mind.
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
RLS is a condition characterised by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. People with ADHD may be more prone to RLS, which can disrupt sleep and cause difficulty in maintaining restful sleep.
Sleep-Related Disorders
Individuals with ADHD may have a higher prevalence of certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnoea or periodic limb movement disorder. These conditions can further impact sleep quality and contribute to daytime sleepiness or fatigue.
To improve sleep quality, individuals with ADHD can try implementing strategies such as:
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Routine
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate the body’s internal clock and improve sleep.
Creating a Calming Bedtime Routine
Engaging in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practising relaxation techniques, can help signal the body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Managing Stimulants
Minimising or avoiding stimulants, such as caffeine or electronics usage, close to bedtime, as they can interfere with falling asleep and disrupt sleep quality.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Keeping the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool can promote a more conducive sleep environment. Additionally, removing distractions like electronic devices can help limit overstimulation.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If sleep difficulties persist and significantly impact daily functioning, it may be helpful to consult a healthcare professional who specialises in sleep disorders. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend specific interventions or treatments tailored to the individual’s needs.
Remember, these strategies may not work the same for everyone, and it’s important to find what works best for you through trial and error. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals can provide personalised recommendations for managing sleep challenges related to ADHD.

6. What Do People With ADHD Lack?
While ADHD is characterised by a set of core symptoms, it is important to note that individuals with ADHD do not necessarily lack anything in a general sense. However, they may experience challenges or difficulties in certain areas due to the symptoms associated with the disorder. Here are some common challenges that individuals with ADHD may face:
Attention and Focus
Individuals with ADHD often struggle with maintaining sustained attention and focusing on tasks. They may have difficulty staying engaged in activities that do not provide immediate stimulation or interest. This can lead to problems with concentration and productivity, particularly in tasks that require sustained mental effort.
Impulsivity
Impulsivity is a hallmark symptom of ADHD. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with inhibiting their impulses, leading to impulsive behaviours or decision-making. This can manifest as interrupting others, acting without thinking about potential consequences, or having difficulty with impulse control in various aspects of life.
Organisation and Time Management
Managing time, planning, and organising tasks can be challenging for individuals with ADHD. They may struggle with prioritising activities, meeting deadlines, and maintaining order in their environment. This can impact their ability to complete tasks efficiently and can lead to difficulties in academic or work settings.
Emotional Regulation
Some individuals with ADHD may experience difficulties regulating their emotions. They may be more prone to mood swings, impulsivity in emotional reactions, or feeling overwhelmed by intense emotions. This can impact their interpersonal relationships and overall emotional well-being.
It is important to note that while individuals with ADHD may face challenges in these areas, they also possess unique strengths and abilities. With appropriate support, strategies, and interventions, individuals with ADHD can learn to manage these challenges effectively and thrive in various aspects of their lives.

7. What Does ADHD Do To The Brain?
ADHD is believed to involve certain differences in brain structure and functioning. While the precise mechanisms are not fully understood, research suggests that ADHD impacts various regions and networks within the brain. Here are some key findings related to the effects of ADHD on the brain:
Prefrontal Cortex
The prefrontal cortex, a region at the front of the brain responsible for executive functions such as attention, impulse control, and decision-making, is often implicated in ADHD. Individuals with ADHD may have smaller prefrontal cortex volumes or exhibit reduced activation in this region during tasks requiring attention and self-regulation.
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia, a group of structures deep within the brain, play a crucial role in motor control, reward processing, and attention. Alterations in the functioning of the basal ganglia have been associated with ADHD. These changes can impact motor coordination, impulsivity, and attentional processes.
Front striatal Circuitry
ADHD is thought to disrupt the front striatal circuitry, a network connecting the prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia. This circuitry is crucial for regulating attention, inhibiting impulses, and modulating cognitive processes. Dysregulation within this network can contribute to the symptoms observed in ADHD.
Neurotransmitters
ADHD has been linked to imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, including dopamine and norepinephrine, which play crucial roles in regulating attention, motivation, and reward processes. These imbalances may impact the transmission and availability of these neurotransmitters in key brain regions.
Connectivity
Studies using brain imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), have shown altered connectivity patterns in individuals with ADHD. Both within-brain connectivity (communication between different regions) and connectivity between brain networks may be affected, leading to difficulties in coordinating and integrating information.
These findings represent broad trends observed in research on ADHD, but they do not apply universally to all individuals with ADHD. The brain is highly complex, and individual differences exist. Furthermore, the relationship between brain differences and ADHD symptoms is still an area of ongoing investigation.
Understanding the impact of ADHD on the brain provides insights into the neural underpinnings of the disorder. However, it is crucial to approach ADHD from a multifaceted perspective, considering not only the neurobiological factors but also psychological, environmental, and social factors that contribute to the manifestation and experience of ADHD.

8. Do People With ADHD Have A Bad Memory?
Memory difficulties can be a common challenge for individuals with ADHD, although the extent and specific nature of memory problems can vary among individuals. Here are some aspects of memory that can be affected by ADHD:
- Working Memory – Working memory refers to the ability to hold and manipulate information in the mind for short periods. Individuals with ADHD often experience difficulties with working memory, which can make it challenging to follow instructions, remember details, or keep track of multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Short-Term Memory – Some individuals with ADHD may have difficulties with short-term memory, which involves retaining information temporarily for immediate use. They may struggle to remember information presented recently or to recall information without immediate cues or reminders.
- Prospective Memory – Prospective memory refers to remembering to perform tasks or activities in the future. Individuals with ADHD may have challenges with prospective memory, leading to forgetting to complete tasks, appointments, or obligations unless they are reminded or have external cues.
- Selective Memory – Individuals with ADHD may exhibit a tendency for selective memory, where they remember certain details or experiences vividly while forgetting others. This can lead to difficulties with recalling specific information when needed or with maintaining consistent attention to important details.
If memory difficulties significantly impact daily functioning, it may be helpful to work with a healthcare professional, such as a psychologist or neuropsychologist, who can conduct a comprehensive assessment and provide appropriate strategies and interventions to support memory function. Strategies such as external reminders, organisation systems, breaking tasks into smaller chunks, and utilising memory aids can also be helpful in managing memory challenges associated with ADHD.

9. Do ADHD Brains Work Faster?
ADHD does not necessarily mean that the brain works faster in all situations. In fact, the relationship between ADHD and the speed of brain processing is more complex and multifaceted.
While individuals with ADHD may exhibit faster processing speeds in certain situations, such as quick thinking or generating ideas, they may also experience challenges with slower processing speeds in other contexts. Here are some important points to consider:
Hyperactivity and Impulsivity
The hyperactive and impulsive symptoms associated with ADHD can create a sense of restlessness and a need for constant stimulation. This can lead to behaviours that appear fast-paced or quick, such as speaking rapidly, engaging in multiple activities simultaneously, or having a tendency to act before thinking.
Attention and Focus
ADHD is often characterised by difficulties in attention and sustained focus. While some individuals with ADHD may have the ability to quickly shift their attention between tasks or stimuli, they can also struggle with maintaining attention for prolonged periods. This can result in challenges with maintaining focus and completing tasks efficiently.
Processing Speed Variability
Individuals with ADHD may exhibit variability in processing speeds. They may experience bursts of rapid cognitive processing in certain situations, while in others, they may face challenges with sluggish or delayed processing. This variability can depend on factors such as task complexity, interest, motivation, and environmental factors.
While some individuals with ADHD may exhibit traits that appear to involve faster cognitive processing, it is not a universal characteristic of ADHD. The experiences and abilities of individuals with ADHD can vary widely, and it is essential to consider the specific strengths and challenges of each person on an individual basis.
Ultimately, ADHD is not solely characterised by fast or slow brain processing speeds but rather by a range of symptoms that affect attention, impulsivity, organisation, and other cognitive functions.

10. Is ADHD Taken Seriously?
Yes, ADHD is taken seriously as a legitimate neurodevelopmental disorder. Over the years, there has been growing recognition and understanding of ADHD within the medical and mental health communities. ADHD is included as a recognised disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which is widely used for diagnosing mental health conditions.
Healthcare professionals, such as psychiatrists, psychologists, paediatricians and neurologists, are trained to assess, diagnose, and treat ADHD. They recognise the impact ADHD can have on individuals’ daily lives, including academic performance, work productivity, relationships, and overall well-being.
Moreover, ADHD is also acknowledged by educational systems, workplaces, and legal frameworks. Many educational institutions have accommodations and support services in place to help students with ADHD succeed academically. Some workplaces provide reasonable accommodations to support employees with ADHD, recognising their unique needs and strengths.
However, it is important to note that there can still be misconceptions or stigmas surrounding ADHD. Some people may misunderstand the disorder, misinterpret symptoms as character flaws or laziness, or believe that ADHD is overdiagnoses or exaggerated. Education and awareness efforts continue to address these misconceptions and promote understanding and support for individuals with ADHD.
It’s crucial to seek professional evaluation and support if you suspect you or someone you know may have ADHD. A qualified healthcare professional can provide a comprehensive assessment, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment options to help manage ADHD symptoms effectively.
“Unlock Your Full Potential: Take Charge of ADHD Today!
At Enlightened Minds, we specialise in comprehensive ADHD assessments and personalised treatment plans that cater to your unique needs. Our team of experienced professionals understands the complexities of ADHD and is dedicated to empowering you on your journey towards success.
Don’t let ADHD hold you back from reaching your true potential. Discover the tools, strategies, and support you need to thrive in all areas of your life. Whether you’re a student striving for academic excellence, a professional seeking greater career satisfaction, or an individual simply longing for a more balanced and fulfilling life, we’re here to help.
Take that crucial step towards a brighter future. Contact us today to schedule your personalised ADHD assessment and embark on a transformational path towards self-understanding, growth, and empowerment.